In the field of civil and structural engineering, deep foundations play a critical role in ensuring stability and load transfer in challenging soil conditions. One common solution engineers often turn to is precast concrete piles. Understanding what precast piles are and how they are used is essential for any construction professional or project stakeholder aiming to ensure safe, cost-effective, and efficient foundation systems.
What are Precast Concrete Piles? Defining Precast Piles
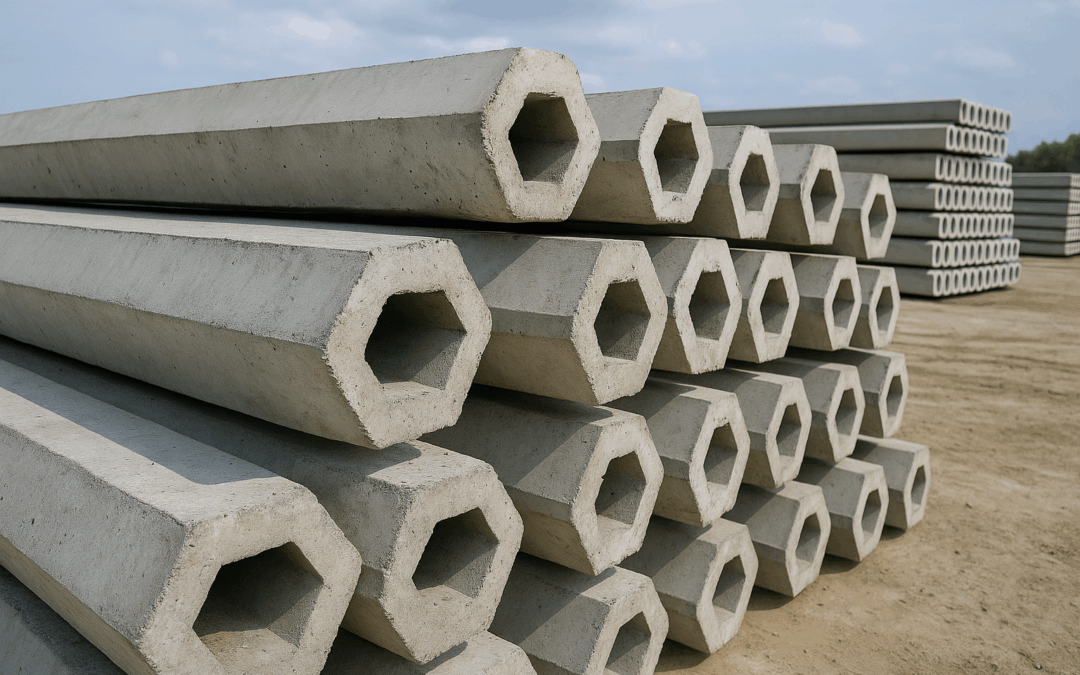
Precast concrete piles are long, slender columns made of high-strength reinforced concrete that are manufactured off-site in controlled environments. Once cured and quality-tested, these piles are transported to the construction site and driven into the ground using heavy pile-driving equipment.
This method ensures uniformity, high durability, and consistent quality, making precast piles an industry standard in deep foundation construction.
According to a comprehensive study by the U.S. Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), precast piles offer significant advantages in terms of strength, speed of installation, and load-bearing capacity compared to cast-in-place options.
Key Characteristics of Precast Concrete Piles
-
Material: Typically composed of high-strength concrete reinforced with steel cages or strands.
-
Shape: Square, round, or octagonal cross-sections, depending on project requirements.
-
Length: Can be manufactured in standard or customized lengths and spliced if deeper penetration is needed.
-
Installation: Driven into the ground by hammers, vibratory drivers, or jacked into place.
Advantages of Using Precast Concrete Piles
Structural and construction benefits include:
-
Consistent Quality: Controlled manufacturing leads to minimal variability and higher reliability.
-
Rapid Installation: No need for onsite curing, minimizing construction timelines.
-
Durability: Resistant to environmental degradation, especially important for marine or coastal applications.
-
High Load Capacity: Suitable for heavy loads, including bridges, high-rise buildings, and industrial facilities.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced labor and project durations can translate into lower overall costs.
Common Applications of Precast Concrete Piles
| Sector | Specific Applications |
|---|---|
| Marine Construction | Piers, wharves, docks, and bulkheads |
| Infrastructure Projects | Bridges, overpasses, highways |
| Commercial Buildings | Foundations for multi-story buildings |
| Industrial Facilities | Warehouses, plants, heavy equipment foundations |
| Coastal and Flood Zones | Protective barriers and structures against erosion |
When it comes to marine and industrial applications, precast piles are indispensable. Their ability to withstand the harsh effects of saltwater, tidal forces, and heavy industrial loads makes them a preferred choice for engineers and developers working in these demanding environments.
Installation Process of Precast Concrete Piles
The general steps for precast pile installation include:
-
Site Survey and Soil Testing: Understanding soil conditions is critical.
-
Pile Manufacturing: Based on project specs, piles are cast and cured in a factory setting.
-
Transportation: Special trucks carry the piles to the site.
-
Pile Driving: Hydraulic hammers or vibratory drivers insert the piles into the ground until reaching refusal or a designated depth.
-
Testing and Quality Assurance: Load testing and inspections ensure compliance with engineering standards.
Proper installation is vital to maximize the structural integrity and performance of precast piles.
Challenges and Considerations
While precast concrete piles offer many benefits, there are certain considerations engineers must account for:
-
Transportation and Handling: Long piles require specialized equipment and careful handling.
-
Driving Limitations: In areas with dense obstructions (e.g., boulders), pile driving can be challenging.
-
Splicing: When greater lengths are needed, splicing techniques must be carefully engineered to maintain structural continuity.
Real-World Example: Marine Infrastructure
An excellent real-world case involves the construction of new marine terminals, where hundreds of precast piles were driven into seabeds to support the massive weight of cargo handling equipment and storage facilities. Their high resistance to saltwater corrosion and dynamic loading conditions demonstrated the unmatched value of using precast concrete in harsh maritime environments.
Understanding Precast Concrete Piles in Modern Construction
Professionals and project managers must appreciate what precast concrete piles offer: durability, consistency, efficiency, and versatility. Whether for marine docks, industrial warehouses, or urban infrastructure, precast piles provide an engineered solution capable of meeting modern construction demands with exceptional reliability.
Understanding their proper application, installation, and maintenance strategies ensures the long-term success and safety of every project where deep foundations are a critical requirement.